Exploring The Magnificence Of The Missouri River
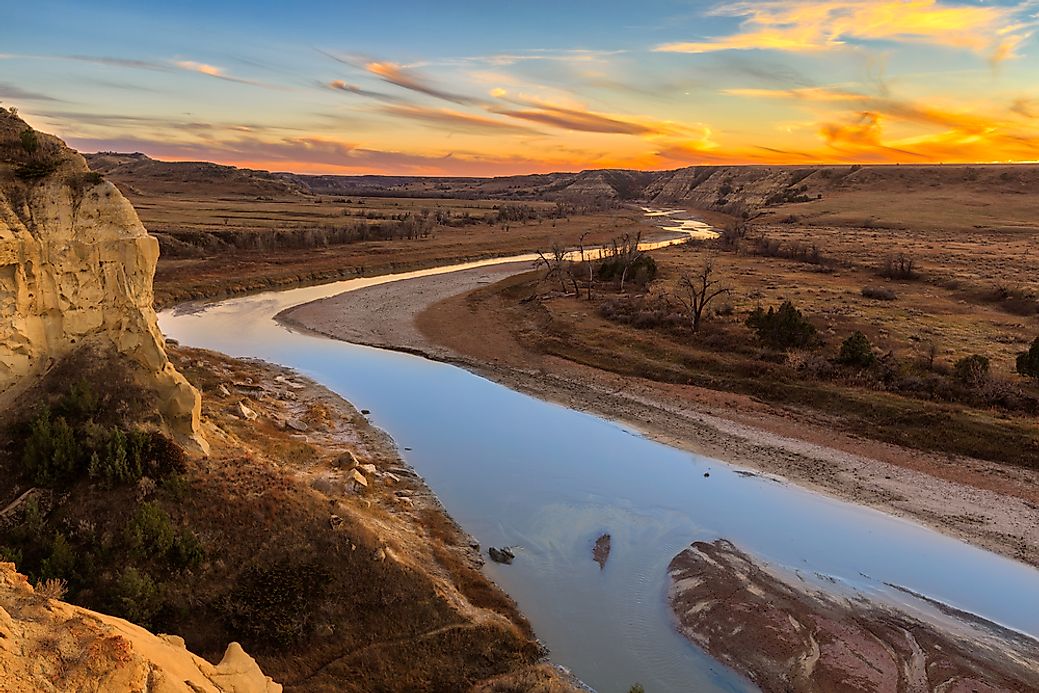
Stretching an impressive 2,341 miles (3,767 kilometers), the Missouri River stands as the longest river in North America, flowing through multiple states and serving as a lifeline for the region. This iconic river, originating in the Rocky Mountains and merging with the Mississippi River, boasts a storied history, diverse ecosystems, and immense economic significance. Understanding its journey from its source to its confluence is crucial to appreciating its pivotal role in shaping North America's landscape.
The Missouri River not only defines the geography of the United States but also sustains numerous communities and industries along its course. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of the Missouri River, exploring its historical legacy, ecological importance, economic contributions, and the recreational opportunities it provides. As we journey through the longest river in North America, we will uncover the intricate connections between this waterway and the people who depend on it.
With its vibrant wildlife and a history marked by exploration and commerce, the Missouri River transcends being merely a geographical feature; it is a lifeline for countless communities. From the indigenous tribes that first called its shores home to the modern cities thriving along its banks, the river has profoundly influenced the culture and economy of the region. Join us as we traverse the heart of North America, discovering the wonders of the Missouri River.
Read also:Discovering The Inspiring Journey Of Kim Sol Mae
Contents Overview
- 1. The Rich History of the Missouri River
- 2. Understanding the Geography and Course
- 3. The River's Ecological Importance
- 4. The Economic Role of the Missouri River
- 5. Recreational Activities Along the River
- 6. Biodiversity Flourishing Along the Missouri River
- 7. Conservation Initiatives for the Missouri River
- 8. Final Thoughts
1. The Rich History of the Missouri River
The Missouri River has a storied past that stretches back thousands of years, playing a central role in the lives of indigenous tribes such as the Sioux, Osage, and Mandan. These tribes relied on the river's resources for sustenance, trade, and cultural significance. The river also played a critical role in the westward expansion of the United States during the 19th century, serving as a vital pathway for settlers and explorers.
One of the most notable expeditions along the Missouri River was led by Lewis and Clark in 1804. Their journey not only mapped the river's course but also documented the rich biodiversity and vast potential of the American West. This expedition laid the groundwork for future exploration and settlement, cementing the river's importance in American history.
1.1 The Missouri River's Influence on American History
Throughout its history, the Missouri River has served as a crucial transportation route, connecting the eastern states with the western territories. This connection facilitated trade, commerce, and the growth of the nation's economy. The river's strategic importance cannot be overstated, as it played a pivotal role in shaping the United States' development.
1.2 Modern Developments Along the River
Today, the Missouri River remains a vital waterway, supporting agriculture, industry, and transportation. Major cities such as St. Louis, Kansas City, and Omaha have flourished along its banks, underscoring the river's enduring significance in American history. Its role in modern infrastructure and commerce continues to evolve, reflecting its adaptability and importance.
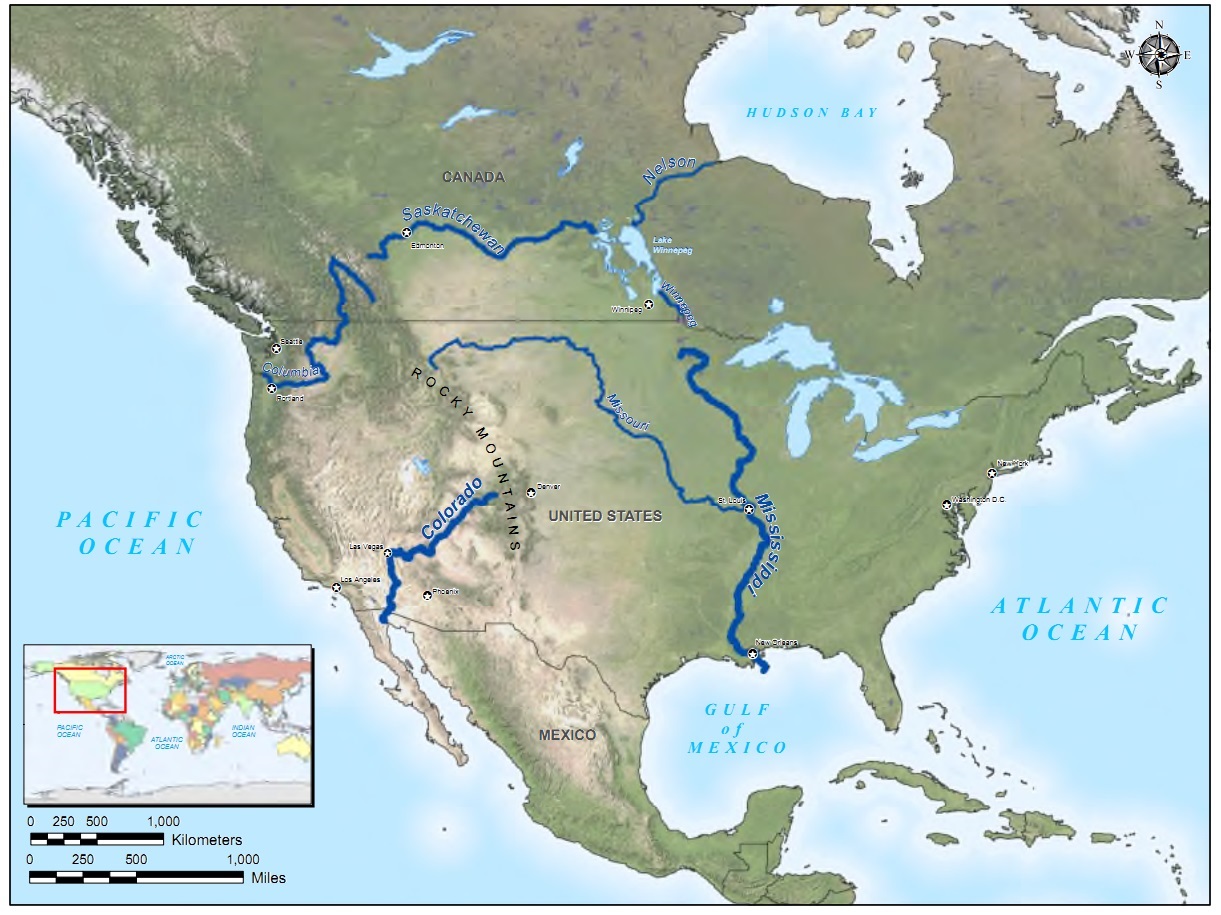
2. Understanding the Geography and Course
The Missouri River begins its journey at the confluence of the Jefferson, Madison, and Gallatin Rivers in Montana, flowing southeast through several states, including North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Iowa, Kansas, and Missouri. It eventually merges with the Mississippi River near St. Louis. The river's course is marked by meandering bends, towering bluffs, and expansive floodplains, creating a diverse range of landscapes along its banks.
The Missouri River Basin spans approximately 529,350 square miles, making it one of the largest river basins in North America. This expansive basin contributes to the river's immense flow and ecological significance, supporting a wide variety of plant and animal life.
Read also:Vinicius Jrs Love Story Discovering The Life And Influence Of His Wife
2.1 Major Tributaries of the Missouri River
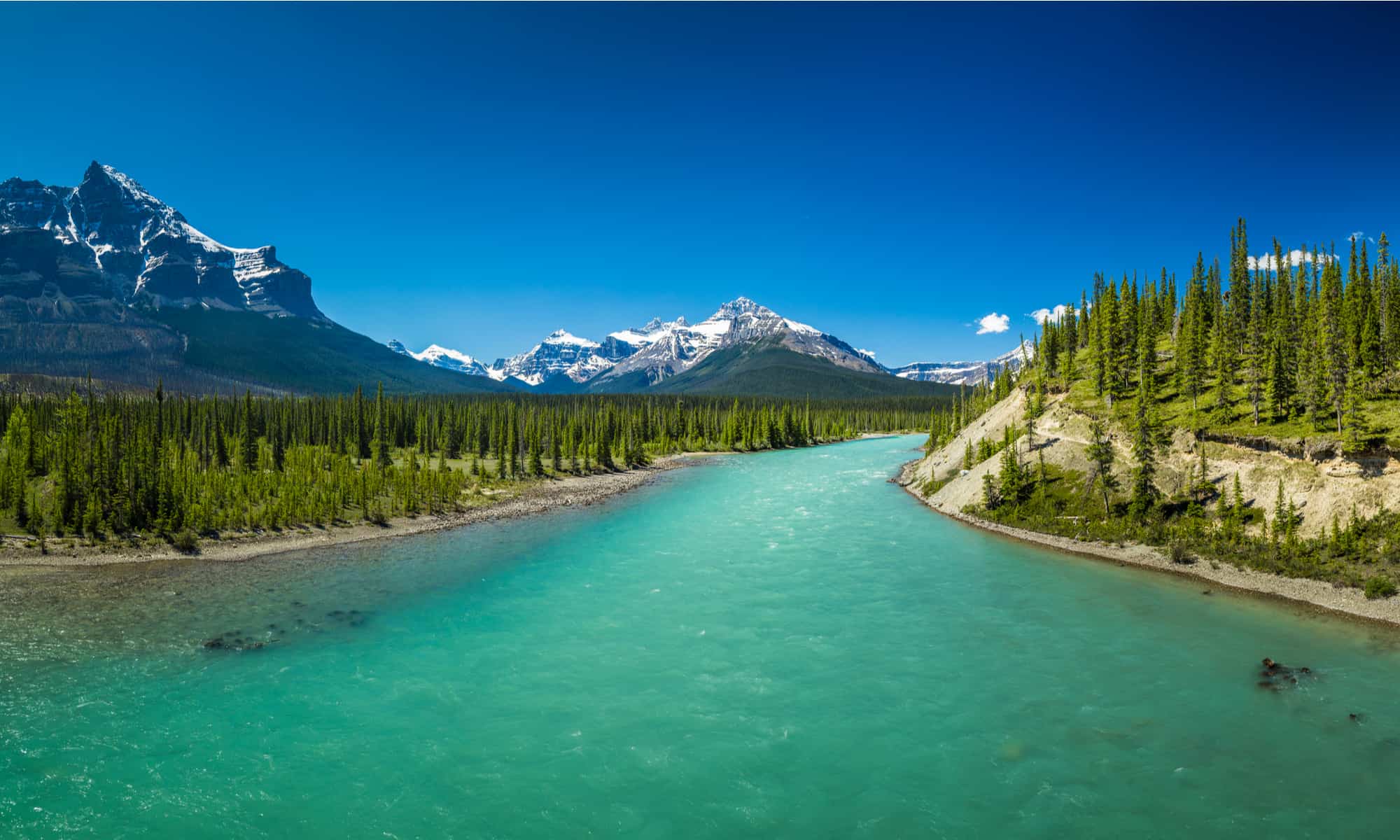
The Missouri River is fed by numerous tributaries, each contributing to its overall flow and ecological health. Notable tributaries include the Yellowstone River, Platte River, and Kansas River. These tributaries enhance the river's complexity and support the diverse ecosystems that thrive along its banks.
2.2 Dams and Reservoir Systems Along the River
To manage flood control, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation, several dams and reservoirs have been constructed along the Missouri River. Prominent dams include the Fort Peck Dam in Montana and the Garrison Dam in North Dakota. These structures play a critical role in regulating the river's flow and supporting the communities that depend on it.
3. The River's Ecological Importance
The Missouri River is home to a rich tapestry of ecosystems, providing vital habitats for countless species of fish, birds, and other wildlife. Wetlands, floodplains, and riparian zones along the river support a remarkable level of biodiversity. Protecting and restoring these ecosystems is essential for maintaining the river's ecological health and ensuring the survival of native species.
Conservation efforts are underway to restore degraded habitats along the Missouri River, focusing on improving water quality and enhancing the living conditions for wildlife. These initiatives are crucial for preserving the river's natural beauty and ecological balance.
3.1 Fish and Wildlife Along the Missouri River
- Fish Species: The river supports a diverse array of fish species, including catfish, bass, and trout, which are integral to the local ecosystem and fishing communities.
- Bird Species: Migratory birds, such as herons and ducks, rely on the river as a critical stopover point during their journeys, highlighting the river's importance in global avian migration patterns.
3.2 Restoring Degraded Habitats
Various conservation organizations are working diligently to restore damaged habitats along the Missouri River. These efforts focus on improving water quality, enhancing vegetation, and creating safe havens for wildlife. By addressing these challenges, conservationists aim to preserve the river's ecological integrity for future generations.
4. The Economic Role of the Missouri River
The Missouri River plays a pivotal role in the economies of the regions it traverses, supporting agriculture, transportation, and tourism. Its waters sustain farming communities through irrigation and crop production, while its transportation routes facilitate the efficient movement of goods. The river's economic contributions are indispensable to the livelihoods of countless individuals and communities.
Agriculture remains one of the primary economic activities along the river, with farmers relying on its waters to nurture their crops. Additionally, the river serves as a vital transportation corridor for barge traffic, reducing costs and supporting regional industries. The economic benefits of the Missouri River extend far beyond its immediate surroundings, impacting national and international markets.
4.1 Transportation and Shipping Along the River
The Missouri River is a critical transportation artery for barge traffic, enabling the efficient movement of goods from inland areas to major markets. This shipping activity reduces transportation costs and supports industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and energy production. The river's role in transportation underscores its importance in the global supply chain.
4.2 Tourism Opportunities Along the Missouri River
- Recreational Activities: The river offers a wide array of recreational opportunities, including fishing, kayaking, canoeing, and hiking, attracting visitors from around the world.
- Historical Tourism: Sites along the river, such as those tied to the Lewis and Clark expedition, draw history enthusiasts eager to explore the river's rich past and its role in shaping the nation.
5. Recreational Activities Along the River
The Missouri River provides a wealth of recreational opportunities for both residents and visitors. Its breathtaking scenery and diverse landscapes make it an ideal destination for outdoor enthusiasts. Whether you're seeking adventure or simply a peaceful escape, the river offers something for everyone.
Popular recreational activities along the Missouri River include fishing, kayaking, canoeing, and hiking along the numerous trails that wind alongside the river. These activities allow individuals to connect with nature and experience the river's beauty firsthand.
5.1 Fishing and Boating Adventures
Fishing is a beloved pastime on the Missouri River, attracting anglers from near and far who seek to catch species such as catfish, walleye, and bass. Boating enthusiasts can explore the river's many bends and coves, offering a unique perspective on its majestic beauty. The river's dynamic nature makes it an exciting destination for those who love water sports and outdoor adventures.
5.2 Scenic Trails and Parks Along the River
Several parks and recreational areas are situated along the Missouri River, providing trails for hiking and biking enthusiasts. These areas often feature picnic spots and scenic overlooks, allowing visitors to enjoy the river's natural splendor. Whether you're seeking a leisurely stroll or a challenging hike, the Missouri River offers trails to suit every interest and ability level.
6. Biodiversity Flourishing Along the Missouri River
The Missouri River is a haven for biodiversity, supporting a rich diversity of plant and animal life. Its various ecosystems, ranging from wetlands to riparian zones, provide critical habitats for countless species, contributing to the overall health of the environment. Protecting and restoring these habitats is essential for maintaining the river's ecological balance and ensuring the survival of native species.
Conservation efforts are crucial for safeguarding the Missouri River's biodiversity and addressing the challenges posed by invasive species and environmental changes. By implementing effective conservation strategies, we can preserve the river's natural beauty and ecological significance for future generations.
6.1 Protecting Endangered Species
Several endangered species depend on the Missouri River for their survival, including the pallid sturgeon and the interior least tern. Conservation programs are in place to protect these species and their habitats, ensuring their continued existence. These efforts highlight the importance of preserving the river's ecosystems for the benefit of all living creatures.
6.2 Managing Invasive Species
The introduction of invasive species poses a significant threat to the Missouri River's ecosystems. Efforts to manage and control these species are essential for preserving the native biodiversity of the river. By addressing this challenge, conservationists aim to maintain the river's ecological balance and protect its unique habitats.
7. Conservation Initiatives for the Missouri River
Conservation organizations and government agencies are actively engaged in protecting the Missouri River and its surrounding ecosystems. These efforts encompass habitat restoration, water quality improvement, and species protection, ensuring the river remains a vital resource for future generations. Public awareness and community involvement are critical components of these initiatives, promoting responsible use of the river's resources.
By fostering collaboration between stakeholders, conservationists aim to create a sustainable future for the Missouri River. This involves implementing effective regulations, engaging local communities, and educating the public about the river's importance and the challenges it faces.
7.1 Encouraging Community Engagement
Community members are encouraged to participate in conservation efforts through volunteer programs, educational workshops, and events focused on river stewardship. These opportunities allow individuals to contribute to the protection and preservation of the Missouri River, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among local residents.
7.2 Government Regulations for River Protection
Government agencies play a vital role in protecting the Missouri River by implementing regulations aimed at preserving water quality and maintaining healthy ecosystems. These regulations ensure that the river remains a vital resource for communities, industries, and wildlife. By enforcing these rules, government agencies help safeguard the river's future and promote sustainable development.
8. Final Thoughts
In summary, the Missouri River is a remarkable natural feature that profoundly impacts the environment, economy, and culture of the regions it touches. Its rich history, ecological significance, and recreational opportunities make it an invaluable asset for the communities that depend on it. By understanding and appreciating the Missouri River's contributions, we can work together to protect and preserve this vital waterway for generations to come.
Article Recommendations